Latest from Green
Sponsored
Red vs. Blue. Tastes Great vs. Less Filling. Kirk vs. Picard. Epic battles for which there really are no right answers. Enter into that pantheon the great debate between flat plate vs. evacuated tube solar thermal collectors. The answer, much to the chagrin of the true believers on either side is ¡ª it depends. Let's first briefly look at the two types of technology.
Flat plate collector: The flat plate collector has been around forever (at least since the 1890s). A flat plate collector is basically an insulated box with glass on one side and copper tubing running through absorber plates.
Evacuated tube collector: Instead of evacuated tube, think thermos bottle. Each tube is actually its own mini-collector. A clear thermos bottle allows sunlight in, an absorber plate absorbs more heat, and the vacuum holds the heat in. Most designs have a heat pipe ¡ª a small diameter, sealed copper pipe inside the thermos bottle. Inside the heat pipe, water, antifreeze, alcohol or some other medium under a mild vacuum flashes to steam around 80¡ãF. So the liquid heats up, turns to steam, rises in the heat pipe to the heat exchanger (usually a larger section of the heat pipe dry fitted to the water- or glycol-carrying header), gives up its heat, turns to liquid, flows to the bottom and repeats the cycle.
Each type has a role to play, depending on where the project is, and what the heating needs are. If you are installing a solar water heater in Phoenix, the flat plate solution is the obvious choice. If you are installing a space heating system in Burlington, Vt., evacuated tubes are the obvious choice. Almost anything in between requires some analysis.
The analysis
To start the analysis, let's look at price, performance and ease of installation.
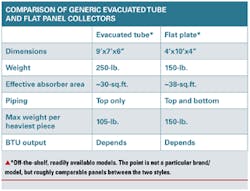
Price: The advantage goes to flat plate collectors, but not by as much as is typically assumed. For example, list prices for the two panels above are flat plate, $1,100; evacuated tube $1,400. How much and if discounts are available from list prices is a whole other subject in the game of solar.
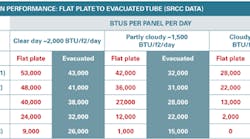
Performance: Regardless of price, how much energy can we get from a panel? Here we will use data from the Solar Rating & Certification Corp. SRCC OG-100 tables. Data for any rated panel can be found here: http://www.solar-rating.org/ratings/og100directories/OG100dirfull.pdf. Because panel performance varies greatly, you should check the specific performance of the panel you are considering.
Now let's compare performance of flat plate to evacuated tube based on SRCC data.
The table above is based on three different sunlight conditions: full sun, partly cloudy and cloudy. At those three conditions, four different temperatures were tested (the temperature is the difference between the outdoor temperature and the water you are heating at the inlet to the collector).
Pool 1 is an estimate of swimming pool heating requirements in a warm climate; Pool 2 is an estimate of pool heating requirements in a cool climate; the same applies to DHW 1 and DHW 2. Black plastic pool panels are recommended for seasonal pool heating.
Somewhere in Row C the performance per panel begins to favor evacuated tube collectors. Note that this compares an approximately 55-sq.ft. evacuated tube panel with an approximately 40-sq.ft. flat panel. If you are minimizing the solar footprint on the roof, flat plates probably win, but you may not get the performance you want in the winter. This graph presents the same information in a slightly different way.
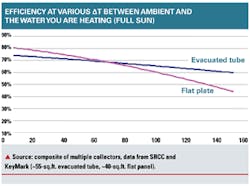
Efficiency crossover point: As you can see from the chart, somewhere between 70¡ãF and 80¡ãF ¦¤T between your incoming water at the solar panel and the ambient air, the evacuated tube is more efficient. An example would be heating 120¡ãF water when it is 40¡ãF outside. The 80¡ãF differential is right at the efficiency crossover. This is a typical case for overnight storage in a solar hot water heater. You want to heat the water to 150¡ãF or higher so you can use that heat energy for nighttime and early morning hot water demand.
However, if your ambient temperature is 50¡ãF or 60¡ãF, then the flat plate is more efficient almost the whole time. The ambient temperature we are considering is the average from 9:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m., the typical ¡°solar window.¡±
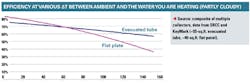
Now let's consider space heating. As a stand-in for winter, we will assume partly cloudy conditions, which will give us approximately 800 Watts/square meter of solar energy.
Under these conditions, the crossover point is about 60¡ãF. If the outdoor temperature during the solar window is 40¡ãF, then heating water to any temperature more than 100¡ãF benefits (at least slightly) from evacuated tube collectors.
Ease of installation: If you are a one-man crew, the evacuated tubes are the hands down winner. Other than that, the flat plate wins. Flat plates are big, heavy and bulky. Full roof harness safety gear for a pitched roof and some sort of mechanical lift are required to get them on the roof safely. A three- to four-man crew can muscle them up by hand, but even with a full crew this is a challenging step in the process.
Both styles require some frame to attach to, and typically require a tilt-angle frame to lift them away from parallel to the roof. The panel or panel header/frame is set in place once the tilt-angle frames are built and installed. It will take a few people to get the flat panel positioned, whereas one person can maneuver the manifold and frame of an evacuated tube collector. While the flat panel is ready for piping, the evacuated tube panel still needs all its tubes put in place (the correct order is complete piping, and then put in tubes). It takes roughly 60 seconds per tube. If you are putting up a single 30-tube evacuated tube collector, that is an additional half hour of time. If you are putting up a 10 collector array, that is an additional five hours.
Miscellaneous considerations
The evacuated tube collector is more efficient at chasing a dwindling resource. So the gross Btus the extra efficiency gets you are not as large, but they may come at the critical time (typically winter conditions).
Windy conditions affect flat panels much more than they do evacuated tubes (due to the surface area of the un-insulated glass). If your project site is typically windy during the day, you might want to give evacuated tube collectors extra consideration.
Evacuated tube collectors only require flow through the header at the top. This can be helpful when installing drainback designs, which are the most efficient freeze-proof designs.
Flat plate panels melt the snow due to their high heat losses through the un-insulated glass. Evacuated tube collectors are so well insulated they do not melt the snow. If the south facing roof at your location does not routinely melt the snow during a typical winter, flat plates are probably a better choice. The evacuated tubes seem to work well under light-to-medium frost. And they will collect energy when half covered with snow (about half as much as when fully exposed).
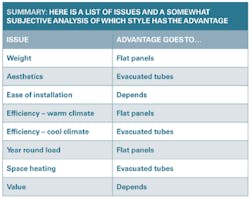
Summary
Below is a list of issues and my somewhat subjective analysis of which style has the advantage.
As the issue can be sliced many ways ¡ª cost per square foot, cost per BTU, performance per square foot of collector, of absorber, of net aperture, etc. ¡ª the debate can be never ending. The Europeans draw graphs similar to the ones presented here. The SRCC data suggests much poorer performance for the evacuated tube panels (SRCC data indicates the crossover point is closer to a 90¡ãF ?T in the graphs above). I am installing data monitoring equipment on a variety of systems, and I hope to revisit this issue with real world results in future articles.
The author is owner of Radiance Heating and Plumbing Inc., www.radianceheating.com, Flagstaff, Ariz. He can be reached at [email protected] or 928-380-6294.